To find dy / dx of y = cos x x Just do the same cos x x = e x ln(cos(x))Or, you can do it a bit differently y = cos x x Take the logarithm of both sides gives ln y = x ln(cos x) Then you can differentiate both sides with respect to x, and see what you getStart your free trial In partnership with You are being redirected to Course Hero I want to submit the same problem to Course Hero CancelIf `y=e^(x) log (sin 2x),` find `(dy)/(dx)`
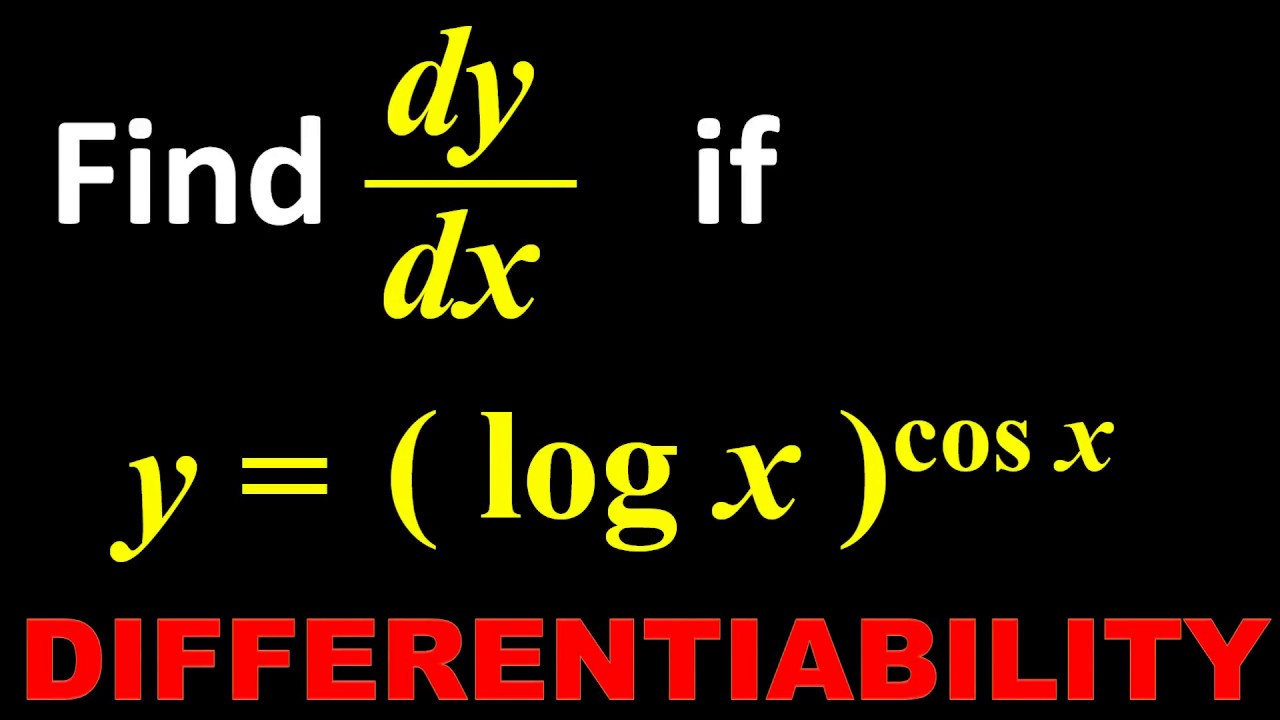
23 Derivative Find Dy By Dx Of Y Log X Cos X Youtube
Find dy/dx if y=cos(log x+e^x)
Find dy/dx if y=cos(log x+e^x)- x cos y dy = (xe x log x e x) dx Integrating both sides, we have This is the required solution of the given differential equationCalculus 1 Answer Epsilon Explanation please see the image file to explanation Answer link Related questions How do I determine the molecular shape of a molecule?



If Y A Cos Log X B Sin Log X Then How Do You Prove That X D Y Dx Dy Dx Y 0 Quora
I need to find $\frac {dy} {dx}$ $$\frac{d} {dx} e^y\cos x=1\sin(xy)$$ using Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 177 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developersIf y = 1 alpha /(1/x alpha) beta /x/(1/x alpha) (1/x betaDerivative of cos(log(x)) by x = sin(log(x))/x Show a step by step solution;
If y = x^tanx root x^2 1/2 find dy/dx;Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Find dy/dx of xy = e^x y Join / Login > 12th > Maths > Continuity and Differentiability Find d x d y of x y = e x − y Medium Video Explanation Answer Given, x y = e x − y Taking logarithm on both the sides, we obtain lo g y = (cos y) x, find d x dWhat is the lewis structure for co2?
Free implicit derivative calculator implicit differentiation solver stepbystepLogy =cos square x×log2 Differentiate both side with respect to x dy/ydx = log2 (2cosx × sinx) 0 (because log2 is constant) dy/dX = (sin2x × log2)/y Put the value of y dy/dX = (sin2x× log2)/ (2^2cos square x) dy/dx = (sin2x × log2) (2^2cos square x) 422 views ·So we'll take the derivative of each side And when we do that, we'll get E to the Y times d y d x times Synnex plus e to the Y times a co sign of X equal to one plus one times y plus x times D Y d X Now this is something that we can work with We have to differentials d Y d X, and what we need is D Y dx by itself




यद Y Cos Log X त Dy Dx Youtube




If Y X 2 Cos Log X Then Find Dy Dx Youtube
We start with the function y = l n ( x) First use exponentiation with the base e to get rid of the log, a common manipulation with log equations, e y = x (*) Now take the derivative of each side, remembering to use the chain rule on ey, because y is a function of x d d x e y = d d x x andFind d2y/dx2 where y=log(x^2/e^2) y=log(x 2 /e 2 ) diff wr to x , we get dy/dx=1/(x 2 /e 2 ) (2x/e 2 ) =2/x diff wr to x again d 2 y/dx 2 =2/x 2 Thank Share with your friends Share 3 Follow 8 Manbar Singh, Meritnation Expert added an answer, on Manbar Singh answered this We have, y = log x cos x x 2 1 x 2 1 Let y = u v where u = log x cos x and v = x 2 1 x 2 1 Now, y = u v ⇒ dy dx = du dx dv dx 1 Let u = log x cos x ⇒ log u = cos x log log x ⇒ 1 u



Lemh105




Y Cos X Log X Find Dy Dx Scholr
Find dy/dx, when If x = e^(cos 2 t) and y = e^(sin 2t), prove that dy/dx = (y log x)/x log yFind the differentiation of the function Differentiate both sides with respect to x to find d y d x in mathematics d y d x = d d x log e ( cos x) There is a direct formula in differential calculus to differentiate the natural logarithmic function d d x log eFind dy/dx by implicit differentiation \cos (xy) = 1 \sin y Video Transcript So for this problem, we're gonna be doing implicit differentiation, which is a very useful technique when dealing with multiple variables in a function or wise and excess all throughout a function




If Cos X Y Cos Y X Find Dydx
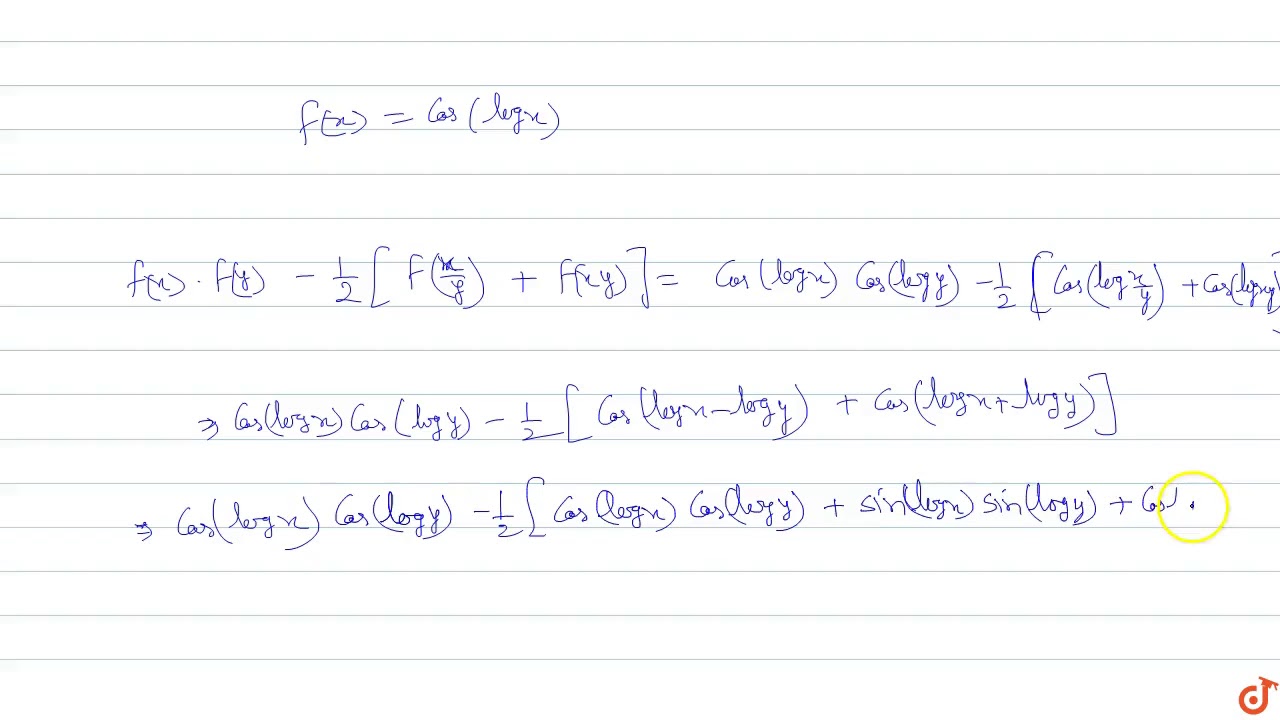



If F X Cos Logx Then F X F Y 1 2 F X Y F Xy Youtube
MATHS DIFFERENTIABILITY Derivative of logarithmic function Easy to understand Useful for Class 10, class11, class 12 Diploma Sem1 m1 EngineeringCBSE, ILet y = log(cos e x) By using the chain rule, we obtain `"dy"/"dx" = "d"/"dx""log"(cos"e"^"x")` `= 1/cos"e"^"x" "d"/"dx"(cos"e"^"x")` ` = 1/(cos"e"^"x") (sin"e"^"x") "d"/"dx" ("e"^"x")` ` = (sin"e"^"x")/(cos"e"^"x") "e"^"x"` `= "e"^"x" tan"e"^"x", "e"^"x" ≠ (2"n"1)pi/2, "n"∈ "N"`Y = e x log x Use product rule dy/dx = e x log x e x (1/x) = e x (log x 1/x) Hence option (2) is the answer
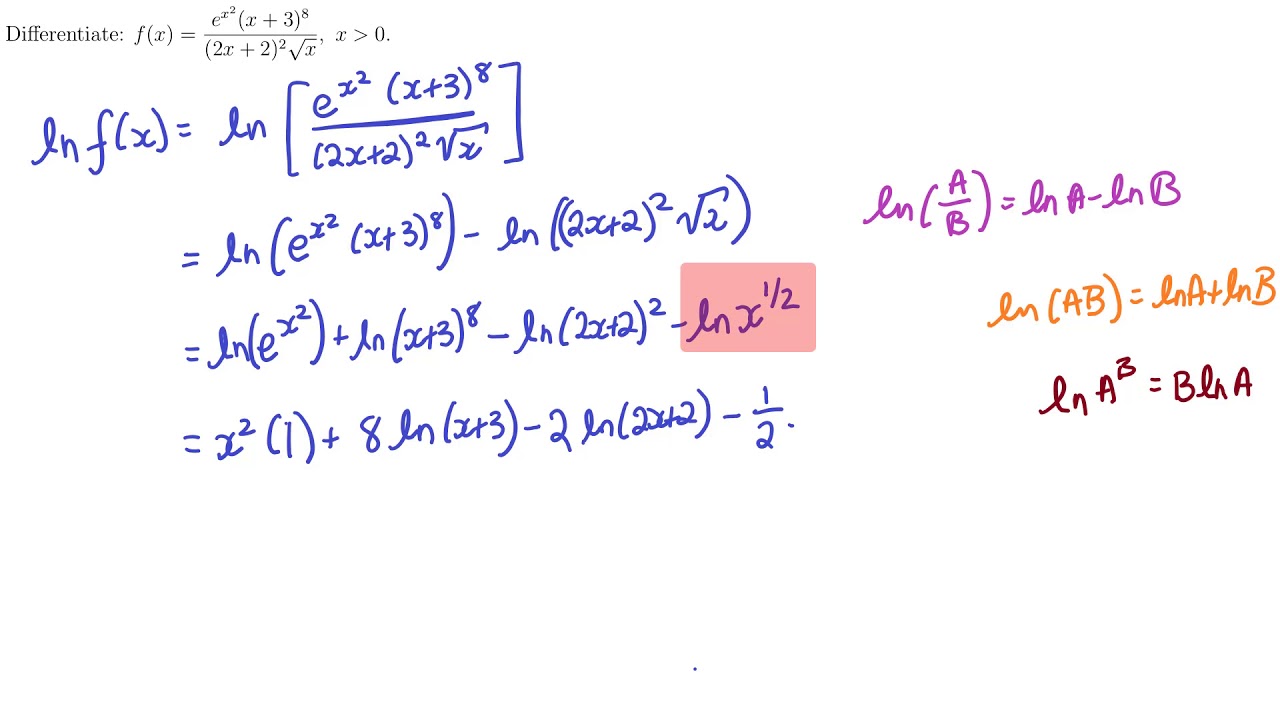



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Ex 5 5 14 Find Dy Dx Of Cos X Y Cos Y X Logarithmic Different
Find stepbystep Calculus solutions and your answer to the following textbook question Find dy / dx by implicit differentiation √x y = x4 y4Answer to Find dy/dx when y = cos(e^x) e^x sin(e^x) (A) dy/dx = e^2x sin(e^x) (b) dy/dx = e^2x cos(e^x) dy/dx = e^2x cos(e^ Skip Navigation Chegg home Ex 54, 10 Differentiate wrt 𝑥 in, cos(log𝑥 𝑒^𝑥), 𝑥 > 0Let 𝑦 = cos(log𝑥 𝑒^𝑥 ) Differentiating both sides 𝑤𝑟𝑡



Is X 2 D 2y Dx 2 3x Dy Dx 5y X 2 Sin Log X Quora




Ipe Material Notes
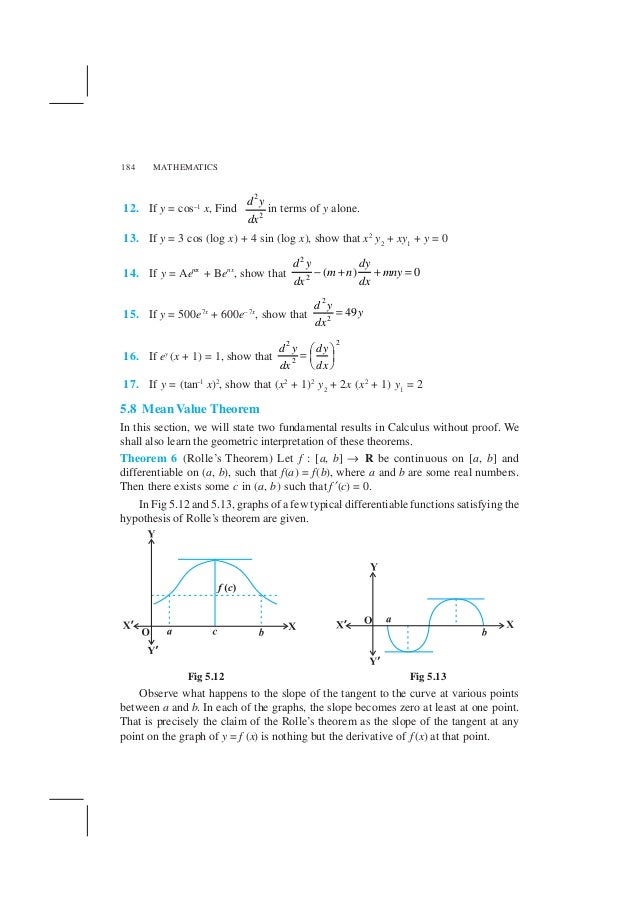
If yx xy xx = ab, find dy/dx If (cos x)y = (cos y)x find dy/dx If cos y = x cos (a y), where cosanot equal plus or minus 1 prove that dy/dx If (xy) e^x/xy = a prove that If x = e^x/y prove that dy/dx = xy/xlogx;If y = cos –1 x, Find 2 2 d y dx in terms of y alone 13 If y = 3 cos (log x) 4 sin (log x), show that x 2 y 2 xy 1 y = 0 14 If y = A e mx B e nx, show that 2 2 0 d y dy m n mny dx dx = 15 If y = 500 e 7 x 600 e – 7 x, show that 2 2 49 d y y dx = 16 If e y (x 1) = 1, show that 2 2 2 d y dy dx dxAttentionlog natural logarithm Draw graph Edit expression Direct link to this page Value at x= Derivative Calculator computes derivatives of a function with respect to given variable using analytical differentiation and displays a stepbystep solution It




Y E X Sin Logx Find Dy Dx Scholr




Eyzqfgnna2tanm
Calculus Find dy/dx y = natural log of cos (x) y = ln (cos(x)) y = ln ( cos ( x)) Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx (ln(cos(x))) d d x ( y) = d d x ( ln ( cos ( x))) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the dy/dx=(e^xe^y)/(e^xe^ysin(y)) We want to dy/dx when cos(y)=e^(xy) Differentiate the left side by the chain rule LHS=d/dxcos(y)=dy/dxsin(y) Differentiate the right side by the chain and product rule RHS=d/dxe^(xy)=d/dxe^xe^y=e^xe^ydy/dxe^xe^y These sides should equal dy/dxsin(y)=e^xe^ydy/dxe^xe^y =>dy/dxe^xe^ydy/dxsin(y)=e^xe^y =>dy/dx(e^xe^ysin(y))=e^xe^y =>dy/dxCalculus Find dy/dx y=e^ (cos (x)) y = ecos(x) y = e cos ( x) Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx (ecos(x)) d d x ( y) = d d x ( e cos ( x)) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps
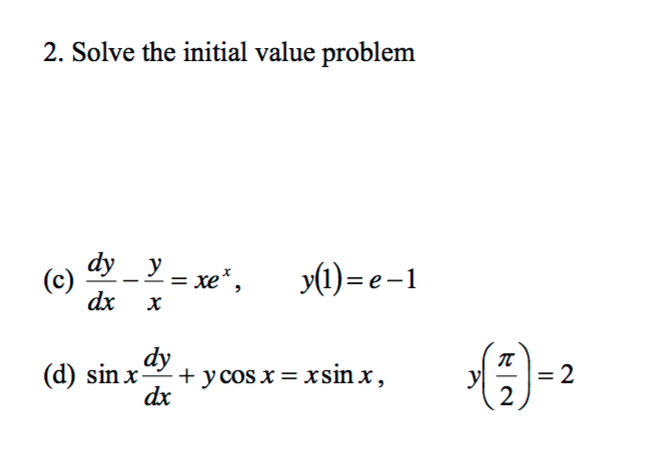



Solve The Initial Value Problem Dy Dx Y X Xe X Chegg Com



Lemh105
U = (logx) x ⇒ log u = log (log x) x ⇒ log u = x log (log x) Differentiating both sides with respect to x, we obtain `1/"u" "du"/"dx" ="d"/"dx" ("x") xx log (log"x")"x""d"/"dx" log (log"x")` `⇒"du"/"dx" = "u" 1xxlog (log"x")"x" 1/log"x""d"/"dx" (log"x")`Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If y = e^x log x sec^2x , then find dydx




Cosx Log Dx Puc Pcmb 2 Cos 1 X2 5 Answer Any Three Questions 3x5 15 Find Dy Dx At X E If Y Cos 1 1 Logx 1 2tanx Dx 3 B Pdf Document




Pdf Engineering Mathematics Ii 15mat21 Surya Karthik Academia Edu
Our online expert tutors can answer this problem Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!So you really need to do a bit more work if you want to use the chain rule Basically, you need to start over, and find the derivative of f (x) = x^u, where u is some function of x, and you will find d/dx (x^u) = x^u (ln (x) (du/dx) u/x) So you find out, shockingly, that theWhat is the lewis structure for hcn?



What Is The Derivative Of Y Cos X Cos X Quora




Find Dy Dx When Y Cosx Logx Youtube
1find dy/dx when sinh 3y=cos 2 x 2calculate dy/dx if Ln(xy)=e^x/y 3calculate dy/dx when xy^3y=3x 4calculate Answered by a verified Math Tutor or Teacher We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our websiteDy dx = f0(x) However, we can treat dy/dx as a fraction and factor out the dx dy = f0(x)dx where dy and dx are called differentialsIfdy/dx can be interpreted as "the slope of a function", then dy is the "rise" and dx is the "run" Another way of looking at it is as follows • dy = the change in y • dx = the change in x `dy/dx=1/(xy log10)cdot(yx cdot dy/dx)` In the line above we have applied the chain rule because `log(xy)` is a composite function On top of that we have applied product rule for `xy` to get




If Y Logx Sin X Then Dy Dx




Ex 5 4 9 Differentiate Cos X Log X Chapter 5 Ncert
Answer to Find dy/dx y*sin(2x) = x*cos(2y) By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework questions You canY = d d x ( sin x × log e x) In this differentiation problem, the variable y represents a function in x Hence, it can be differentiated with respect to x and do not think that y is a constant Therefore, the function y can be differentiated by the derivative rule of logarithms 1 y × d y d x = d d x ( sinHere we will use cot (x) = cos (x)/sin (x) cosec 2 (x) = 1 cot 2 (x) Chain rule dy/dt * dt/ dx = dy/ dx Product rule d/dx (u v) = u dv/dx v*du/dx x = cot (y)=




Solve The Following Differential Equation Xcosydy Xe Xlogx E X Dx



If Y A Cos Log X B Sin Log X Then How Do You Prove That X D Y Dx Dy Dx Y 0 Quora
Ex 56, 8 If x and y are connected parametrically by the equations without eliminating the parameter, Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥, 𝑥 = 𝑎 (cos〖𝑡log〖 tan〗〖𝑡/2〗 〗 ) , 𝑦=𝑎 sin𝑡Here 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑡)/ (𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑡) Calculating 𝒅𝒚/𝒅𝒕 𝑦 = 𝑎 sin𝑡 𝑑𝑦Solution For Find (dy)/(dx) in the followingy=sin^(1)((2x)/(1x^2)) Differentiate the following wrt x sin x e x Find d x d y in the following y = sec − 1 (2 x 2 − 1 1 ) Find d x d y , if y sin y = cos x For what value ofIf x = cot (y) what is dy/dx?




Document Maxima And Minima Mathematical Concepts




Find Dy Dx If Y E A X Secx Logx Sqrt 1 2x
Dy = c 1 cosh x dx y = c 1 sinh x c 2 # 2 e x x dx x = x y'' cos2x = 2y and obtain the general solution to the above differential equation 2 ndOrder ODE 17 3 Homogeneous Equations with Constant Coefficients y'' a y' b y = 0 where a and b are real constants Find dy/dx in the following e^(x y) = log(x/y) Sarthaks eConnect Largest Online Education Community Find \(\cfrac{dy}{d\mathrm x} \) in the following ex y = log\(\Big(\cfrac{\mathrm x}{y}\Big)\) Login Remember Register Test JEELogy=log(cosx)^cotx logy=cotxlog(cosx) (1/y)dy/dx=cotx{(1/cosx)sinx}log(cosx)cosec²x dy/dx={1cosec²xlog(cosx)}y dy/dx={1cosec²xlog(cosx)}(cosx)^cotx



Derivatives Of Sin X Cos X Tan X Eˣ Ln X Video Khan Academy



If X A Cos 8 Log Tan 8 2 And Y A Sin 8 Then What Is Dy Dx At 8 P 4 Quora
Answer to Use implicit differentiation to find frac{dy}{dx} of the curve ysin(x^2y^2)=xy1 By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep for Teachers for Schools for Working Scholars Stack Exchange network consists of 177 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange Find #dy/dx#of #y=x^logx (log x)^x#?




Cos Log X E X Novocom Top




If Y Cos X 2 E X Then Dy Dx
Differentiation of inverse function by chain rule Differentiation by substitution Differentiation Of Implicit Functions Find differentiation of a r c sin x using first principle Find differentiation of a r c cos x using first principle Derivation of all well known results Diffrentiate e 2 x and e sin xThe derivative of the function `y = log(x 1/x)` with respect to x, `dy/dx` has to be determined It is assumed that log in the problem refers to natural logarithm Use the chain rule here Derivative of y = ln u (where u is a function of x) Unfortunately, we can only use the logarithm laws to help us in a limited number of logarithm differentiation question types Most often, we need to find the derivative of a logarithm of some function of xFor example, we may need to find the derivative of y = 2 ln (3x 2 − 1) We need the following formula to solve such




Cosx Log Dx Puc Pcmb 2 Cos 1 X2 5 Answer Any Three Questions 3x5 15 Find Dy Dx At X E If Y Cos 1 1 Logx 1 2tanx Dx 3 B Pdf Document




If Y A X E X X X X A Find Dy Dx At X A




Find The Derivatives W R T X X Sec X Log X E X




If Cos 1 Y B Log X N N Find The Value Of X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx N 2y Youtube




If Y Cos Log X Then D 2 Y Dx 2



Solve The Differential Equations D 2y Dx 2 2dy Dx Y Xe X Cos X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If X Cos Logt Y Log Cost Then Dy Dx Youtube
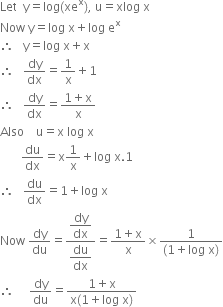



Differentiate Log X Ex W R T X Log X From Mathematics Continuity And Differentiability Class 12 Cbse



Studentstars Files Wordpress Com 14 09 Sem1 2 Engineering Mathematics1 Unit1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Pdf
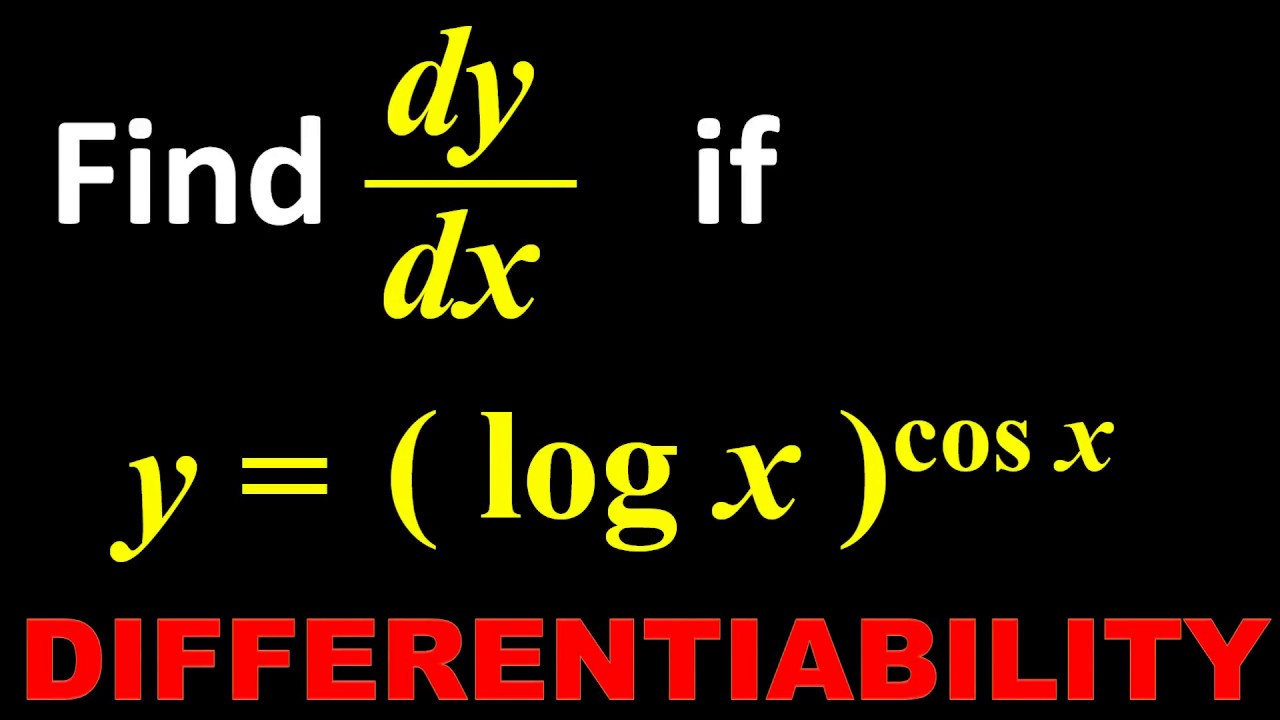



23 Derivative Find Dy By Dx Of Y Log X Cos X Youtube
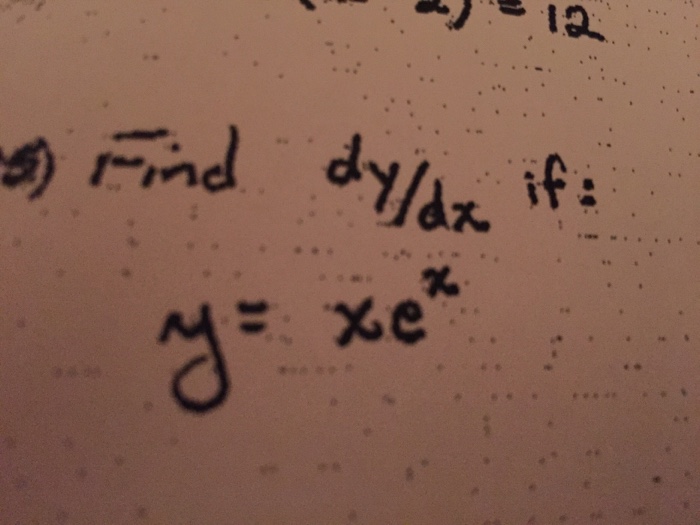



Find Dy Dx If Y Xe X Chegg Com




Example 29 Differentiate I E X Ii Sin Log X Iii Cos 1 E X




If Y Log Tan X 2 Find Dy Dx Brainly In




Cosx Log Dx Puc Pcmb 2 Cos 1 X2 5 Answer Any Three Questions 3x5 15 Find Dy Dx At X E If Y Cos 1 1 Logx 1 2tanx Dx 3 B



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Find Dy Dx If X Cos Log T And Y Log Cos T




Ipe Material Notes




If Y E Tan X Log X Tan X Then Find Dy Dx Youtube



What Is The Solution Of X D 3xd 1 Y Sin Log X Quora
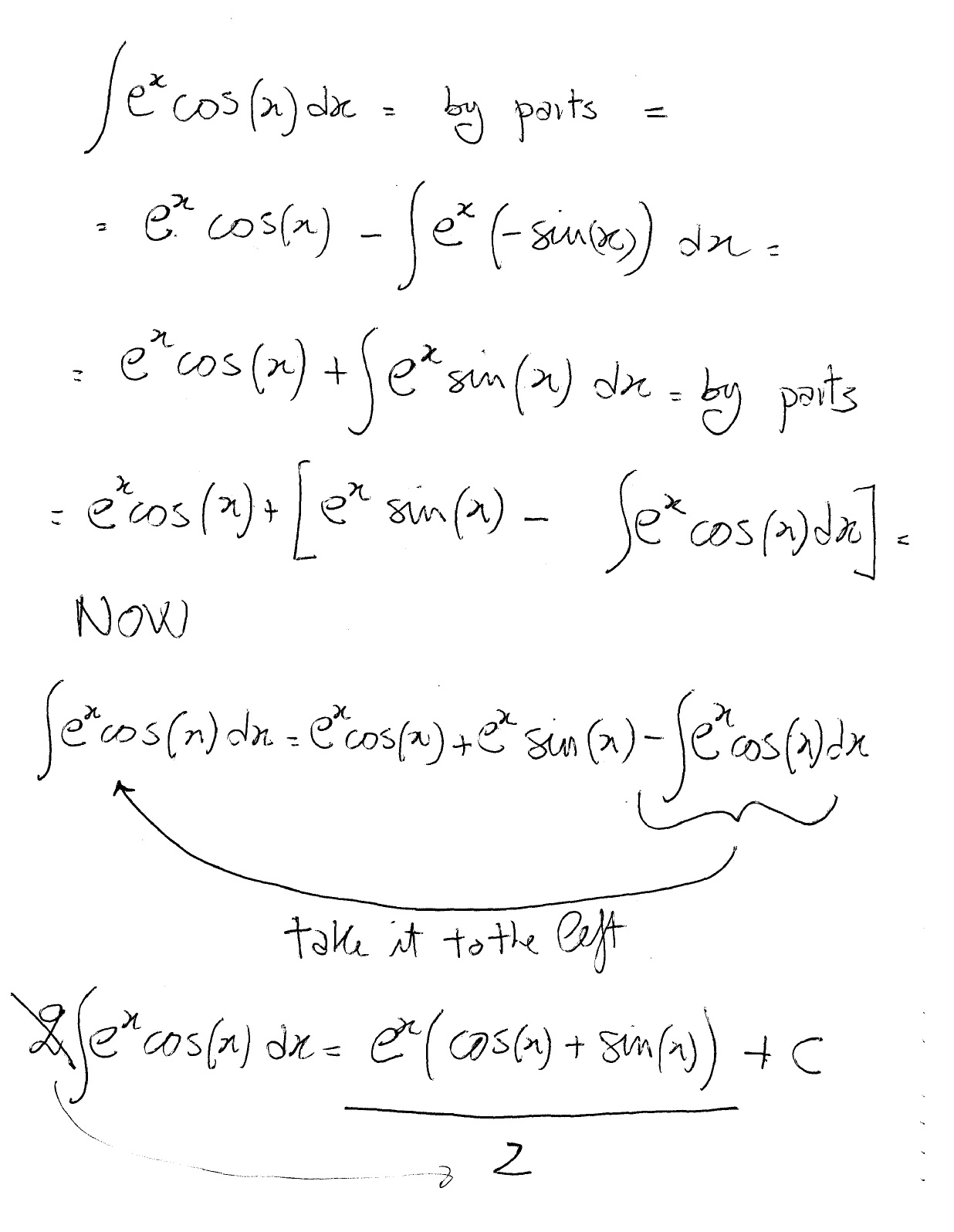



How Do You Find The Integral Of E X Cosx Dx Socratic




Ex 5 5 3 Differentiate The Function Log X Cos X Teachoo




How To Integrate Xe X Steps Tutorial Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




The Derivative Of X 2 1 Log X E X Cos X W R T X Is




Find The Derivative Of Yw R T X Where Y Log Cosx X E X 2




Ex 5 2 8 Differentiate Cos Root X With Respect To X




Ipe Material Notes




Particular Integral Of X 2 Y Xy 4y Cos Ln X X Cdot Sin Ln X Mathematics Stack Exchange
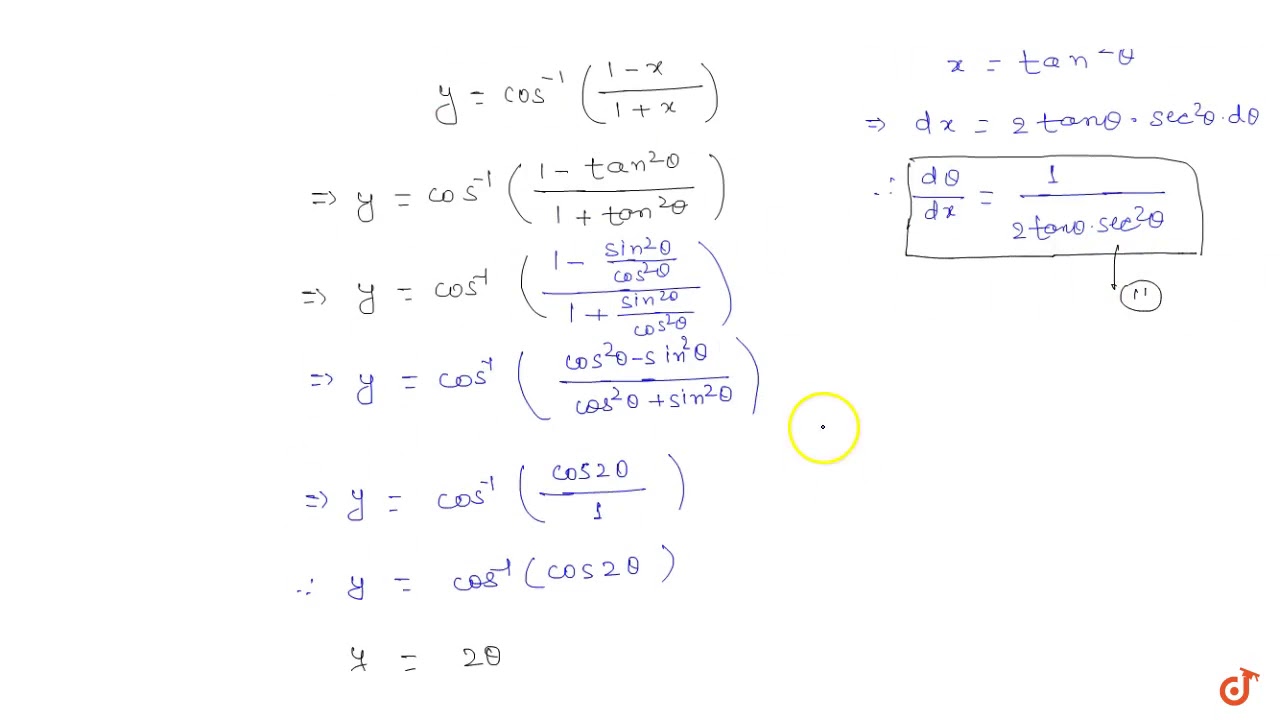



If Y Cos 1 1 X 1 X Then Find Dy Dx Youtube




If Y Log 1 Cos 2 X1 E 2x Show That Dydx E 2x 1 E 2x Sinxcosx 1 Cos 2 X



Www Masterjeeclasses Com Wp Content Uploads 19 01 7 Methods Of Differentiation And Applications Of Derivativesexercise Pdf



If X Y E X Y Show That Dy Dx Logx Log Xe 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



If X Ecos2t And Y Esin2t Prove That Dy Dy Y Log X Log Y Studyrankersonline




Find Dy Dx Of X Cos Y Sin X Y Socratic




Ex 5 3 11 Find Dy Dx In Y Cos 1 1 X2 1 X2 Ex 5 3



What Is The Solution Of X D 3xd 1 Y Sin Log X Quora




Evaluate Dydx Xe X Logx E Xx Cos Y




If Y A Cos Log X Sin Log X Then X 2y2 Xy1




Ex 5 4 10 Differentiate W R T X In Cos Log X E X Teachoo



If Y Sin Log X Then Prove That X 2 D 2y Dx 2 Dy Dx Y 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y E X Log Sin 2x Find Dy Dx




Show That Y A Cos Log X B Sin Log X Is A Solution Of The Differential Equation X 2 D 2y Youtube



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation



How To Solve Math X 3d 3 3x 2d 2 Xd 1 Y Cos Log X Math Quora
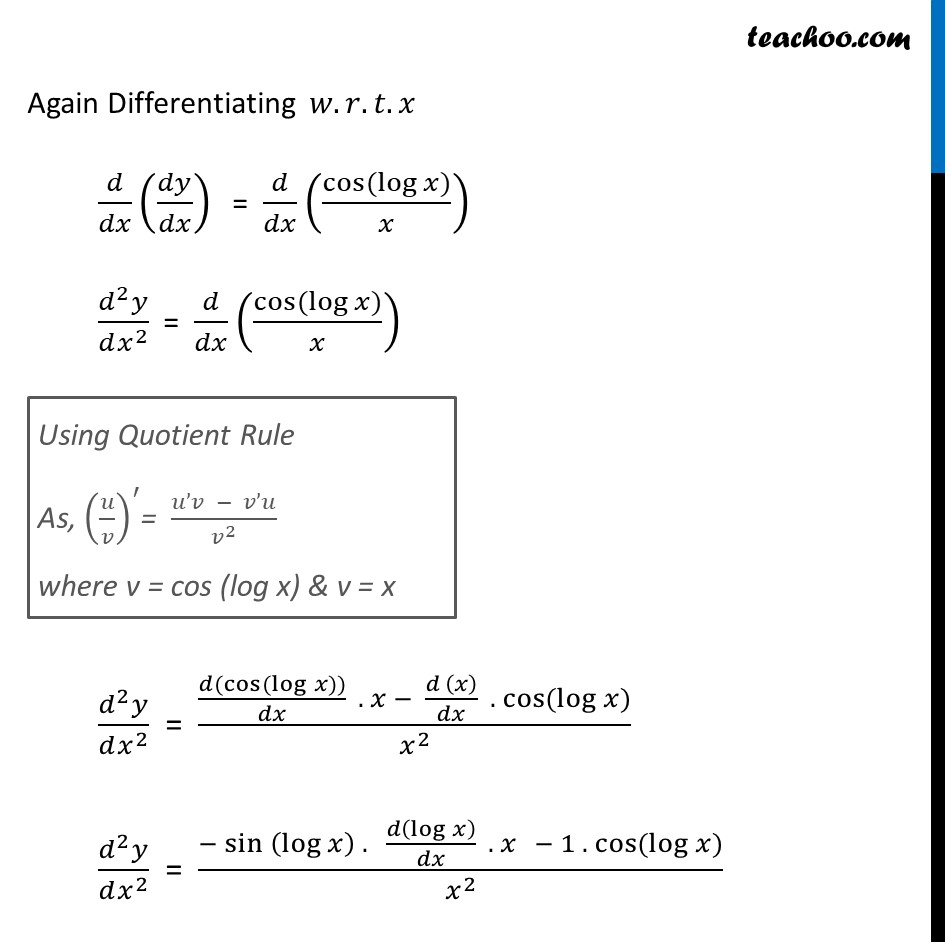



Ex 5 7 10 Find Second Order Derivatives Of Sin Log X




Ex 5 5 3 Differentiate The Function Log X Cos X Teachoo




Worked Example Differentiating Related Functions Video Khan Academy




1 Find The Derivative Of Each Function A E E 7 Chegg Com



How To Evaluate Math Int Sin Log X Cos Log X Cdot Dx Math Quora




Differentiation Ex 1 1 Q 2 Maharashtra State Board Mathematics And Statistic For Arts And Science




Derivatives Of Sin X Cos X Tan X Eˣ Ln X Video Khan Academy



Studentstars Files Wordpress Com 14 09 Sem1 2 Engineering Mathematics1 Unit1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Pdf




Find Dy Dx If E X Y Cos X Y Brainly In



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy



What Is The Bisection Method Where F X Cosx X E X Quora
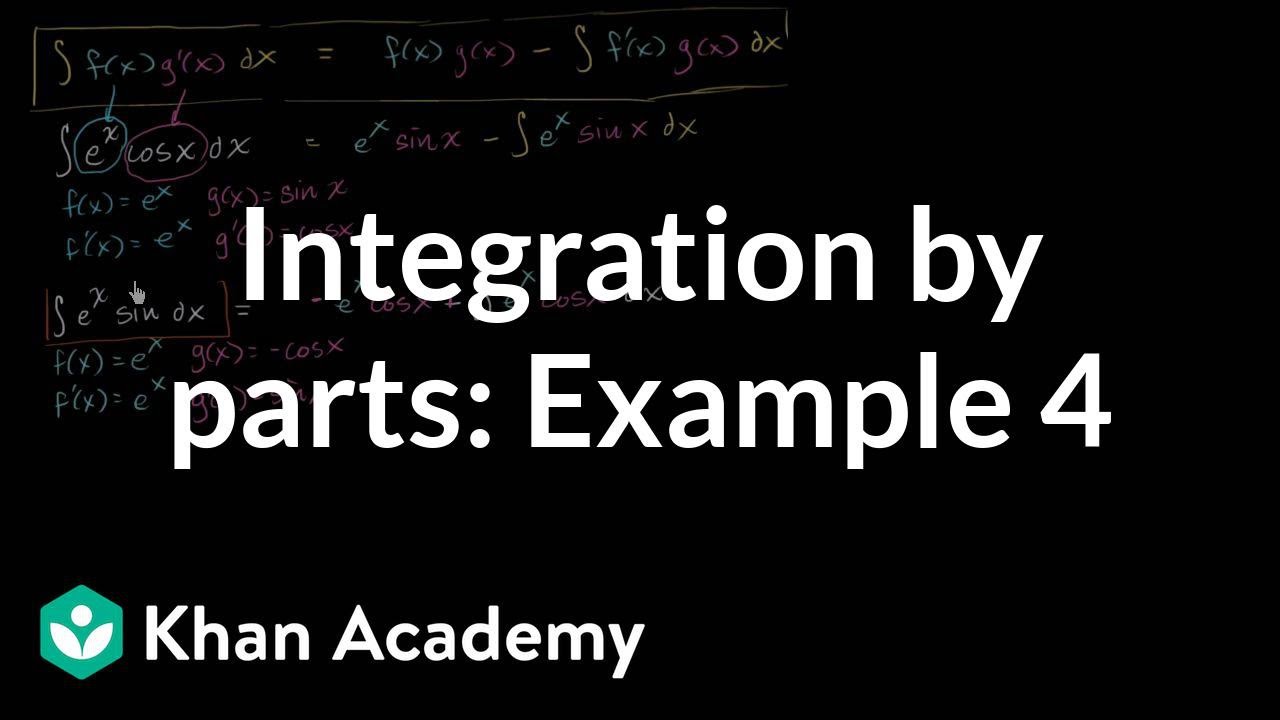



Integration By Parts 𝑒ˣ Cos X Dx Video Khan Academy
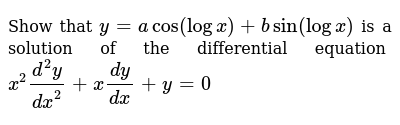



Show That Y A Cos Log X B Sin Log X Is A Solution Of The Diffe




If Y Log Cos Tan 1 E X E X 2 Then Dy Dx Brainly In



Www Amherst Edu Media View Original Ma11fall09finalanswers Pdf




2xxdah6tiitzmm



How To Solve Math X 3d 3 3x 2d 2 Xd 1 Y Cos Log X Math Quora




Ipe Material Notes




Maths Pages 51 100 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



Solve The Following Differential Equation X Cos Y Dy Xex Log X Ex Dx Mathematics Topperlearning Com Rn73oni66




Derivative Rules For Y Cos X And Y Tan X Calculus Socratic




Differentiate The Following W R T X Cos Log X Ex X 0 Mathematics Shaalaa Com




Eyzqfgnna2tanm



5 22 Find Dy Dx By Implicit Differentiation 5 X2 Chegg Com




Find Derivative Of Cos Logx E X X 0 W R T To X




Find The Derivatives W R T X X Sec X Log X E X Youtube




Differentiate The Following Functions With Respect To X I



The Solution Of Dy Dx X Log X 2 X Sin Y Y Cos Y Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y Cos Log Cot X Then Find Frac D Y D X



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿